Collagen Peptides: Molecular Formula and Structure:
-(C₆H₁₂O₆N₂₄)n
-Gly-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Gly-Pro-Hyp-...
Collagen is a long-chain protein formed by three helices, each chain composed of amino acids, primarily glycine, hydroxyproline, and proline.










Collagen Peptides: Molecular Formula and Structure:
-(C₆H₁₂O₆N₂₄)n
-Gly-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Gly-Pro-Hyp-...
Collagen is a long-chain protein formed by three helices, each chain composed of amino acids, primarily glycine, hydroxyproline, and proline.
Collagen peptides are partial hydrolysis products of collagen, typically obtained from collagen through enzymatic digestion. Collagen, a protein mainly found in connective tissues, plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue structure, elasticity, and tensile strength in the human body. The hydrolysis process breaks down long chains of collagen into shorter peptide segments, which are more easily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Due to their relatively small molecular weight, collagen peptides are considered to be more readily absorbed through the intestinal mucosa into the bloodstream.
Intake of collagen peptides is thought to benefit the health of skin, joints, bones, and other connective tissues.
Collagen peptides positively impact skin and health issues caused by cellular aging by regulating the extracellular matrix and intracellular signaling pathways at the cellular level and promoting skin elasticity, moisture balance, and repair regeneration at the biological level. Supplementation with collagen peptides is believed to promote the production of collagen, slowing down skin laxity and wrinkle formation, making the skin appear more moisturized and youthful.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
a. Role of Collagen in the Extracellular Matrix:
Collagen primarily exists in the extracellular matrix, forming a supportive structure that provides structural support to cells. Supplementing with collagen peptides may increase the elasticity and stability of the extracellular matrix, combating extracellular matrix aging and laxity.
b. Collagen Synthesis and Secretion:
Collagen within cells is synthesized through protein synthesis mechanisms. The intake of collagen peptides may stimulate the synthesis and secretion of collagen within cells, increasing the collagen content in the extracellular matrix.
c. Regulation of Cellular Signaling Pathways:
Collagen peptides may regulate cellular signaling pathways by binding to cell surface receptors, affecting cell proliferation, differentiation, and repair functions.
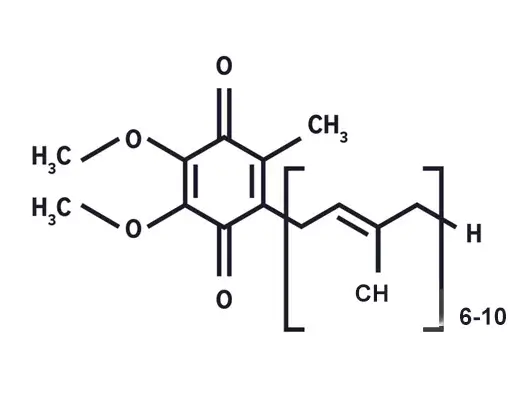
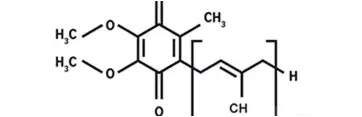
Coenzyme Q10: Molecular Formula and Structure:
-C59H90O4
-H2C=CH-C(CH3)=CH-C(CH2-O-)=C(CH2-O-)-C(CH2-C5H5N)=CH-C(CH3)=CH-C(CH2-C5H5N)=CH-C(CH3)=CH-C(CH2-C5H5N)=O
The molecular structure of Coenzyme Q10 mainly includes a long, repeating monomer-based quinone chain, typically denoted as Q, and a coenzyme part, usually a respiratory framework, used for interaction with the electron transport chain in mitochondria.
Coenzyme Q10 positively improves skin and health issues caused by cellular aging through various pathways, including antioxidation, energy production, and maintaining cell membrane stability, at the cellular and tissue level.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
a. Antioxidant Mechanism:
Coenzyme Q10 acts as an antioxidant within cells, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress damage to cells. This helps to slow down the process of cellular aging, especially under external environmental stress.
b. Mitochondrial Energy Production:
Coenzyme Q10 is involved in the mitochondrial respiratory chain's Complex I, II, III, and IV, driving ATP production within cells. This is crucial for providing the energy required by cells, supporting normal cell functions.
c. Cell Membrane Stability:
Coenzyme Q10 may play a role in maintaining cell membrane stability, helping to preserve the integrity of cells.

Vitamin B: Molecular Formulas:
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): C12H17N4OS
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): C17H20N4O6
Vitamin B3 (Niacin or Nicotinic Acid): C6H5NO2
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): C9H16NO5
-Promoting Skin Health: The B vitamins play an important role in the growth, maintenance, and repair of the skin, helping to maintain its health.
-Slowing Skin Aging: Some B vitamins, like Vitamin B3 (Niacin), have antioxidant properties, which can slow down the skin aging process and promote collagen production.
-Maintaining Skin Moisture Balance: Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) helps maintain the skin's natural moisturizing function, combating skin dryness.
-Reducing Inflammation: Some members of the B vitamins, such as Vitamin B3, have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce skin inflammation and may positively affect skin issues like acne.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Energy Metabolism: The B vitamins are key factors in energy metabolism, participating in the metabolism of glucose, fats, and proteins, maintaining normal cellular energy supply.
-DNA Synthesis and Repair: The B vitamins play a vital role in DNA synthesis and repair, maintaining the integrity of cellular genetic information.
-Neurological Function: Vitamins B1, B6, B9, B12 are crucial for the normal functioning of the nervous system, maintaining the health of nerve cells and normal neurotransmission.
-Formation of Red Blood Cells: Some members of the B vitamins, such as B6, B9, and B12, are involved in the formation of red blood cells, crucial for healthy blood and oxygen transportation to tissues.
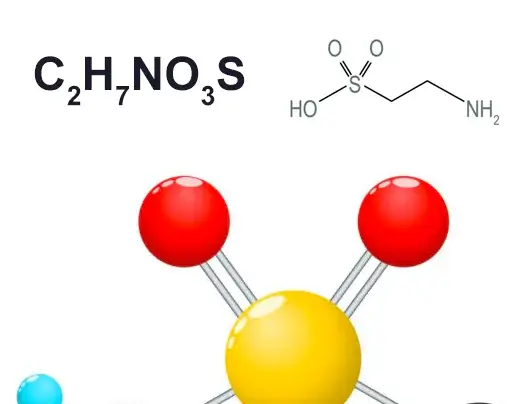
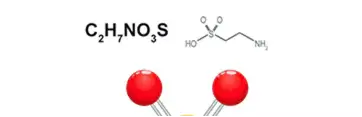
Taurine: Molecular Formula and Structure:
Molecular Formula: C2H7NO3S
Structure: Includes an aminomethyl group (-CH2-SO3H) and an amino group (-NH2).
Numerous studies have found that taurine is an active substance that regulates normal physiological activities of the body, with various biological functions such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, maintaining osmotic balance, supporting normal visual function, regulating cellular calcium balance, lowering blood sugar, regulating neurotransmission, participating in endocrine activities, regulating lipid digestion and absorption, increasing cardiac contractility, enhancing immune capabilities, strengthening the antioxidant capacity of cell membranes, and protecting myocardial cells.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
A study published in the journal Science found that a lack of taurine in the human body may lead to aging. The study indicates that taurine may reduce cellular aging, prevent telomerase deficiency, inhibit mitochondrial dysfunction, reduce DNA damage, and alleviate inflammation.

Curcumin: Molecular Formula and Structure:
Molecular Formula: C21H20O6
Structure: Curcumin's molecular structure includes two benzene rings and an α,β-unsaturated β-diketone.
Curcumin is widely used in traditional medicine and herbalism. It has multiple biological activities, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Research suggests that curcumin may positively impact cardiovascular health, immune systems, and neurological systems.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Anti-Inflammatory Action: Curcumin reduces the release of inflammatory factors by inhibiting inflammatory pathways such as the NF-κB signaling pathway. This alleviates cellular inflammation, lowers chronic inflammation levels, and helps maintain cellular homeostasis.
-Gastric Mucosal Protection: With its antioxidative properties, curcumin may help protect the gastric mucosa from oxidative damage, slowing the aging of gastric tissues.
-Immune Modulation: Curcumin has been found to potentially affect the activity of immune cells, aiding in regulating the immune system's response.

Magnesium Glycinate: Molecular Formula:
-Mg(C2H4NO2)2·H2O
Magnesium glycinate has multiple benefits. It helps promote muscle relaxation, alleviate muscle tension and fatigue, and improve sleep quality by shortening the time to fall asleep. Additionally, it benefits cardiovascular health, helping to maintain normal heart rhythm and blood pressure levels. It may also enhance stress resilience, alleviate anxiety, and have a positive impact on emotional and mental health. It regulates bone health and energy metabolism as well.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Improving Sleep Quality: Magnesium affects the nervous system and can regulate neurotransmitter release. It may increase the levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), thereby producing calming and sleep-inducing effects.
-Cardiovascular Health: Magnesium is involved in regulating the electrical activity of myocardial cells, maintaining normal heart rhythm. Additionally, magnesium has vasodilatory effects, which can help lower blood pressure.
-Bone Health: Magnesium is a crucial component in bone tissue, participating in bone mineralization and metabolism. It can influence the activity of bone cells, promoting the formation and maintenance of bone tissue.
-Muscle Relaxation: Magnesium, as an important intracellular ion, participates in regulating muscle contraction and relaxation. It can bind with ATP to form magnesium-ATP complexes, thereby regulating muscle energy metabolism.

Vitamin E: Molecular Formula and Structure:
C29H50O2
Primarily composed of a benzene ring, a side chain, and a saturated side chain, with the hydroxyl group providing antioxidative activity.
Note: The most common and biologically active form is α-tocopherol (alpha-tocopherol).
As a vital antioxidant, Vitamin E plays a key role in maintaining cell membrane integrity and preventing damage to biomolecules by free radicals. Studies show that Vitamin E has positive effects on cardiovascular health, immune system support, skin and eye health, and may have a modulatory role in anti-inflammatory processes.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Antioxidative Action: Vitamin E, a lipid-soluble antioxidant, can neutralize free radicals in cell membranes. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules produced by oxidation processes and can damage biological molecules such as cell membranes, proteins, and nucleic acids. Vitamin E stabilizes free radicals by donating electrons, preventing further oxidative chain reactions, thus protecting cells from oxidative stress.
-Maintaining Cell Membrane Integrity: The cell membrane is the outer structure that envelops and protects the inside of the cell. Vitamin E protects the lipid structure of the cell membrane by inhibiting lipid peroxidation reactions, maintaining its integrity, which is crucial for normal cell function and stability.
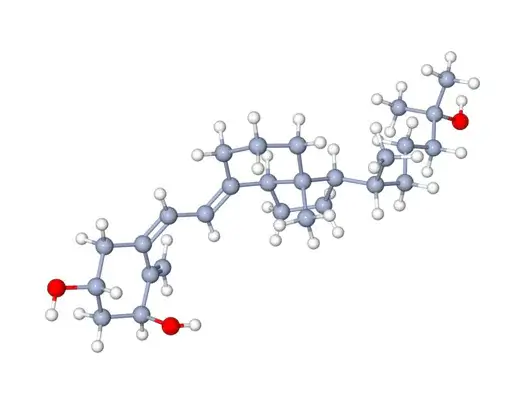
Vitamin D3: Molecular Formula and Structure:
-C27H44O
-Structure: Comprises a four-ring structure and a side chain, containing a lipophilic cyclopentane skeleton.
-Bone Health: Vitamin D3 is crucial for bone health as it promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, maintaining the mineralization process of bones. Adequate levels of vitamin D3 help prevent fractures, osteomalacia, and other bone-related issues.
-Immune System Support: Vitamin D3 participates in regulating immune system functions, aiding in resisting infections and diseases. It can influence the activity of immune cells, essential for maintaining immune system balance and normal function.
-Cardiovascular Health: Some studies suggest that vitamin D3 may be related to cardiovascular health and have a positive impact on the cardiovascular system. It may help reduce the risk of hypertension and maintain vascular health.
-Nervous System Support: Vitamin D3 is involved in the normal functioning of the nervous system and may impact the protection and transmission of nerve cells. Some studies also suggest that vitamin D3 is related to the risk of neurological diseases.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Bone Health: One of the primary functions of vitamin D3 is to promote the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. In intestinal cells, vitamin D3 enters the cell nucleus by binding to the vitamin D receptor (VDR), activating genes that increase the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, thus promoting bone mineralization.
-Immune System Regulation: Vitamin D3 is also expressed in immune cells with vitamin D receptors. It regulates immune cell functions, such as inhibiting T cell activity and modulating inflammatory responses, thus maintaining immune system balance. This helps prevent excessive immune reactions and autoimmune diseases.
-Cardiovascular Health: Vitamin D3 may positively affect cardiovascular system cell functions, impacting vascular wall relaxation and inhibiting inflammatory responses. It may also be involved in blood pressure regulation.
-Nervous System Support: Vitamin D receptors are expressed in various parts of the nervous system. Vitamin D3 may impact the normal functioning of the nervous system, either directly or indirectly. This could include protecting neurons and regulating neurotransmission.
Probiotics: Molecular Formula and Structure:
Probiotics are microorganisms, so they do not have a specific molecular formula or structure. Instead, their biological characteristics are of interest, including their ability to survive in the gut and interact with the host's gut microbiota.
Probiotics are beneficial live bacteria or active yeasts that are considered to have positive effects on gut health. These microorganisms mainly include lactobacilli (such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacteria) and yeasts like Saccharomyces boulardii.
Probiotics have various positive impacts on health, mainly including maintaining gut microbiota balance, enhancing immune system function, promoting nutrient absorption, alleviating intestinal inflammation, reducing allergic reactions, and potentially having a positive impact on mood and mental health. By regulating the microbial community in the gut, probiotics help prevent and alleviate gastrointestinal issues and are closely related to physiological processes such as immune regulation and nutrient absorption, supporting overall health.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Maintaining Gut Microbiota Balance: Probiotics help maintain a balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut through mechanisms such as competitive exclusion of pathogens, production of antimicrobial substances, and modulation of gut pH.
-Enhancing Immune System: The gut is a crucial part of the immune system. Probiotics interact with the gut mucosal layer, activating immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes, thereby enhancing the activity of the immune system.
-Promoting Nutrient Absorption: Some probiotics can secrete enzymes that participate in the breakdown and digestion of food, thereby enhancing the absorption of nutrients from the food.
-Alleviating Intestinal Inflammation: Probiotics may alleviate intestinal inflammation by modulating immune responses, reducing the release of inflammatory mediators, and maintaining the integrity of the gut mucosal barrier.

Silymarin: Molecular Formula and Structure:
Silybin A: C25H22O10
Silybin B: C25H22O10
Structure: The molecular structure includes multiple benzene rings and hydroxyl groups.
-Liver Protection: Silymarin is widely used for liver protection, helping maintain liver cell health and reducing the impact of liver damage.
-Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidative: Silymarin may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects on chronic inflammation and oxidative stress throughout the body.
-Cardiovascular Health: Some studies suggest that silymarin may positively impact cardiovascular health, including reducing cholesterol levels and anti-thrombotic effects.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Liver Protection: Silymarin is shown to have a protective effect on the liver, potentially through mechanisms such as regulating the redox balance in liver cells and inhibiting fibrosis. At the liver cell level, silymarin may protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, reduce inflammation, and help maintain normal liver cell functions.
-Cardiovascular Health: Silymarin is believed to lower cholesterol levels and inhibit platelet aggregation, positively affecting the cardiovascular system. The reduction in cholesterol may involve silymarin's impact on cholesterol synthesis and metabolism in liver cells.

Vitamin C: Molecular Formula and Structure:
Molecular Formula: C₆H₈O₆
Structure: Vitamin C has a relatively simple molecular structure, containing six carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms. Its structure includes a six-membered ring, making it a cyclic molecule. The molecular structure of vitamin C contains two hydroxyl groups (-OH) and one ketone group (C=O), which give it antioxidant properties.
Vitamin C exhibits potent antioxidant effects in the skin, slowing skin aging, enhancing elasticity, reducing age spots, and promoting collagen synthesis. It also supports the immune system, enhancing the body's ability to resist infections, with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, aiding in maintaining vascular health and promoting cellular repair. Vitamin C plays a significant role in both physical health and skincare.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Antioxidant Action: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals, slowing oxidative stress, and preventing free radical damage to cell membranes, DNA, and proteins.
-Cell Membrane Stability: Vitamin C helps maintain the stability of cell membranes, protecting cells from external harmful substances.
-Iron Reduction: Vitamin C can reduce iron ions from Fe^3+ to Fe^2+, enhancing the absorption of non-heme iron and promoting normal iron transport in the blood.
-Collagen Synthesis: Vitamin C participates in collagen synthesis, playing a crucial role in maintaining the health of skin, blood vessels, bones, and other structures.
-Immune System Support: Vitamin C promotes the normal function of white blood cells, enhancing the immune system's resistance, aiding in combating infections and diseases.
-Inhibiting Melanin Production: Vitamin C regulates the activity of tyrosinase, inhibiting melanin production and helping to reduce pigmentation issues.

Grape Seed Extract: Main Components Include:
-Flavonoids: Including proanthocyanidins, resveratrol, etc. These compounds are potent antioxidants, helping to neutralize free radicals and slow down oxidation reactions.
-Proanthocyanidins: One of the main components in grape seed extract, belonging to the class of flavonoids, with powerful antioxidant effects.
-Polyphenols: Including various polyphenolic compounds, such as catechins, which are also antioxidants.
-Antioxidant Protection: The proanthocyanidins and other antioxidant components in grape seeds help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, thereby slowing down the skin aging process.
-Promoting Collagen Production: Antioxidants help maintain the structure of collagen and promote its production, thereby helping to maintain skin elasticity and firmness.
-Reducing Inflammatory Responses: Components in grape seeds may have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce skin inflammation, such as redness and itching.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Affecting Cellular Signaling Pathways: Compounds like flavonoids may regulate cellular signaling pathways, affecting cellular metabolism and functions, including regulating inflammation and immune responses.
-Inhibiting Oxidative Stress: Antioxidant components help suppress oxidative stress reactions, maintaining intracellular redox balance, contributing to cell health.

Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Molecular Formulas:
Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): C18H30O2
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): C20H30O2
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): C22H32O2
-Heart Health: Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce triglyceride levels in the blood, decrease platelet aggregation, thereby lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases. They also lower blood pressure and positively affect the electrical activity of the heart.
-Anti-Inflammatory: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to alleviate chronic inflammation, important for preventing and mitigating many chronic diseases, including arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
-Neural Development: Especially during fetal and infant development, Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for the normal development of the brain and eyes. DHA is a major structural fatty acid in the brain and retina.
-Improving Mood and Cognitive Function: Omega-3 fatty acids are associated with mental health. Studies suggest their role in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improving cognitive functions. EPA and DHA, in particular, may have a positive impact on brain structure and function.
Cellular and Biological Mechanism of Action:
-Regulation of Cell Membranes: Omega-3 fatty acids are important components of cell membranes, especially DHA in neural cells. They affect membrane fluidity and stability, which are related to cell signaling and receptor functions, thus affecting normal neuronal activities.
-Inflammation Regulation: Omega-3 fatty acids exert their anti-inflammatory effects by affecting inflammatory pathways. They competitively replace precursors of inflammatory mediators, such as arachidonic acid (AA), reducing the production of pro-inflammatory substances and alleviating chronic inflammatory responses.
-Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Omega-3 fatty acids are precursors in neurotransmitter synthesis, particularly DHA in relation to neurotransmitters such as dopamine and adrenaline. This may positively affect normal transmission in brain neurons and the stability of the nervous system.

DrBioCare
Collagen Peptide & Magnesium Glycinate
Multivitamin Mineral Supplement